Adding a New Script, Editing or Deleting Scripts
Important! To add a new script, edit, or delete a script, a user role with Manage Scripts permission is required.
Adding a New Script to the Library
- Navigate to Configuration | Script Library.
- Select + New Script to launch the wizard.
- On the General step, enter the script name and description.
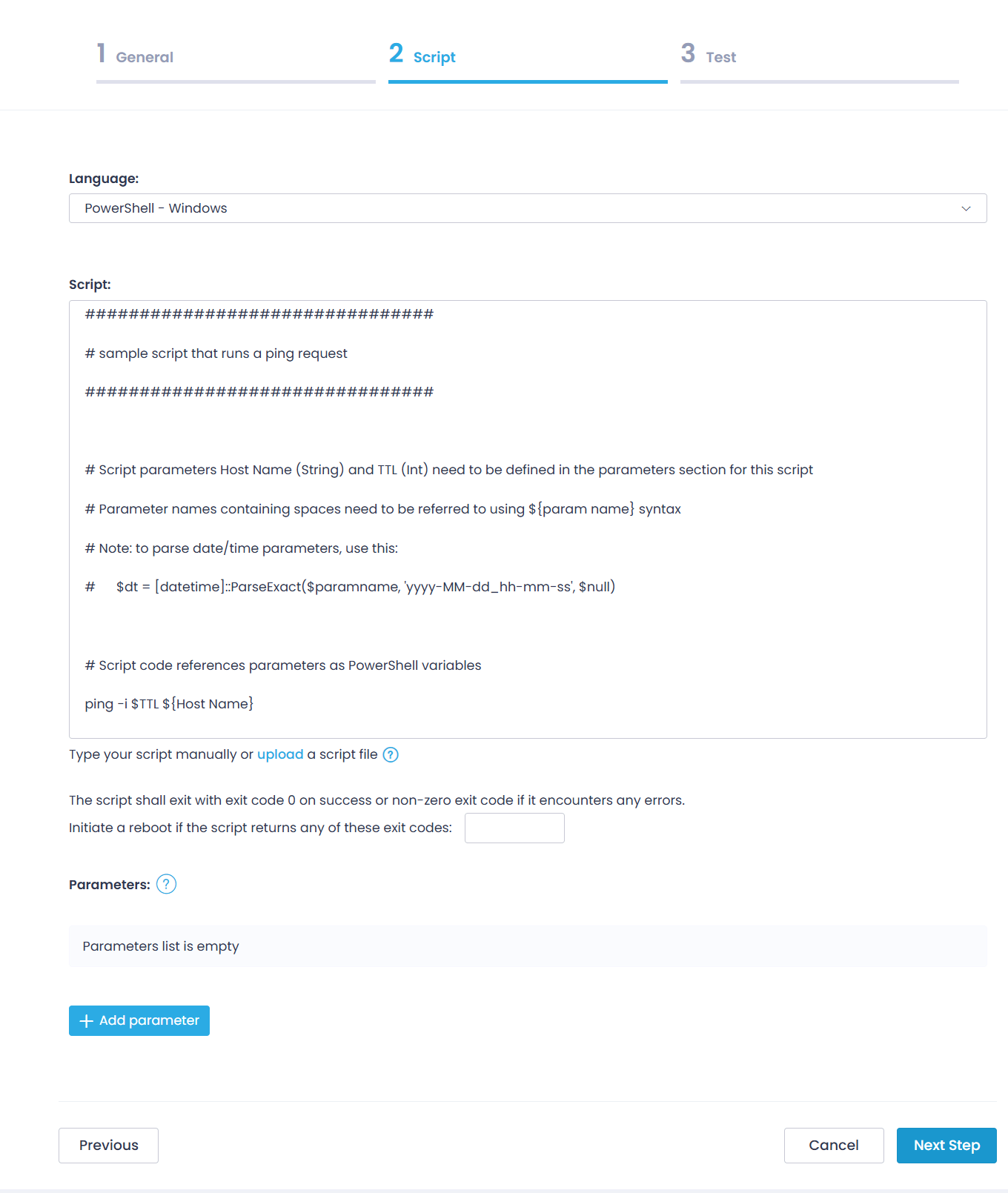
- On the Script step:
-
- Specify the script language (PowerShell, CMD, or Bash). To learn more about certain script types, refer to the Examples section below.
- Enter your script. You can type in the script body or upload a file.
-
NOTE: The upload option is recommended if you are using signed scripts. See Script Signing for details.
-
-
- If necessary, specify exit codes for your script. It is recommended that your script exits:
- with exit code 0 on success
- with non-zero exit code if it encounters any error. In this case, you can instruct Action1 to initiate a reboot of the target endpoint.
- (for PowerShell and CMD scripts) In the Parameters section, click + Add parameter and specify the name, default value, and type for each parameter used in the script.
- If necessary, specify exit codes for your script. It is recommended that your script exits:
-
Tip: You can also provide new parameter values when configuring an automation to run this script.
NOTE: Configuration options for the Bash script parameters are not available within the wizard. You must specify parameter names and values in the script body. See the Examples section for details.
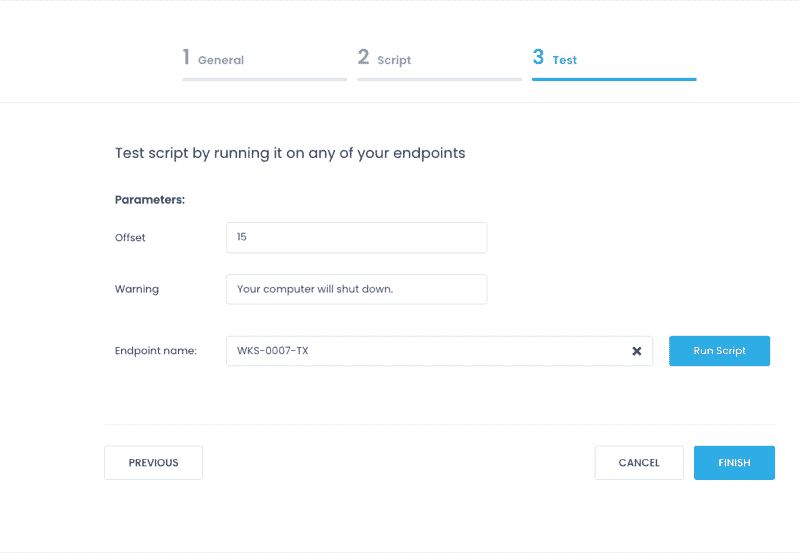
- On the Test step, verify the script operation. Select the target endpoint and click Run Script.
NOTE: If necessary, you can modify parameter values on this step.
- Wait for the script execution to complete. Verify the results and finish the wizard.
A new custom script will appear in the Script Library.
Examples
Example 1: PowerShell
- On the General step of the New Script wizard, enter:
-
- “Ping Host” as Name
- “Send a ping to the specified host.” as Description
-
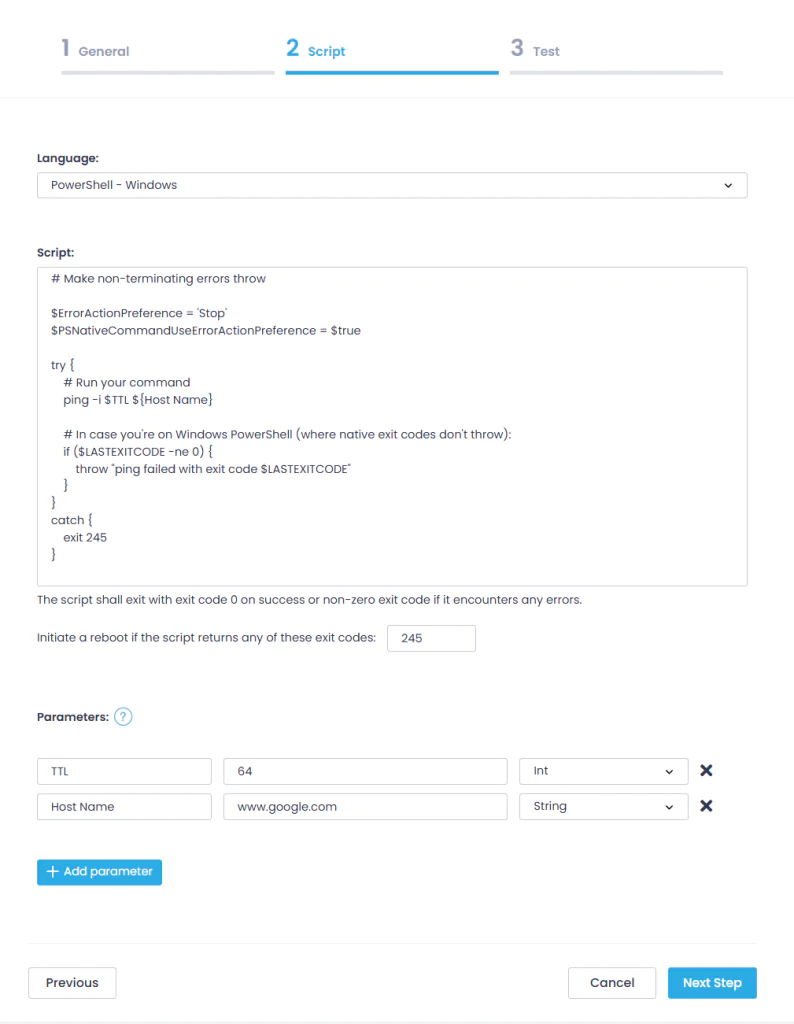
- On the Script step, enter a sample PowerShell script:
# Make non-terminating errors throw:
$ErrorActionPreference = 'Stop' $PSNativeCommandUseErrorActionPreference = $true try
{
# Run ping command
ping -i $TTL ${Host Name}
# In case where native exit codes don't throw:
if ($LASTEXITCODE -ne 0){
throw "ping failed with exit code $LASTEXITCODE"
}
}
catch {
exit 245
}
NOTE: If a parameter name contains a space, enclose it in brackets as ${param name}, e.g., ${Host Name}
- In the Parameters section, click +Add parameter and define TTL and Host Name parameters, providing their names, default values, and types:
- Set TTL type to Int and value to 64
- Set Host Name type to String and value to www.google.com
- If you want to initiate a reboot if the script fails, enter the exit code other than 0, e.g., 245.
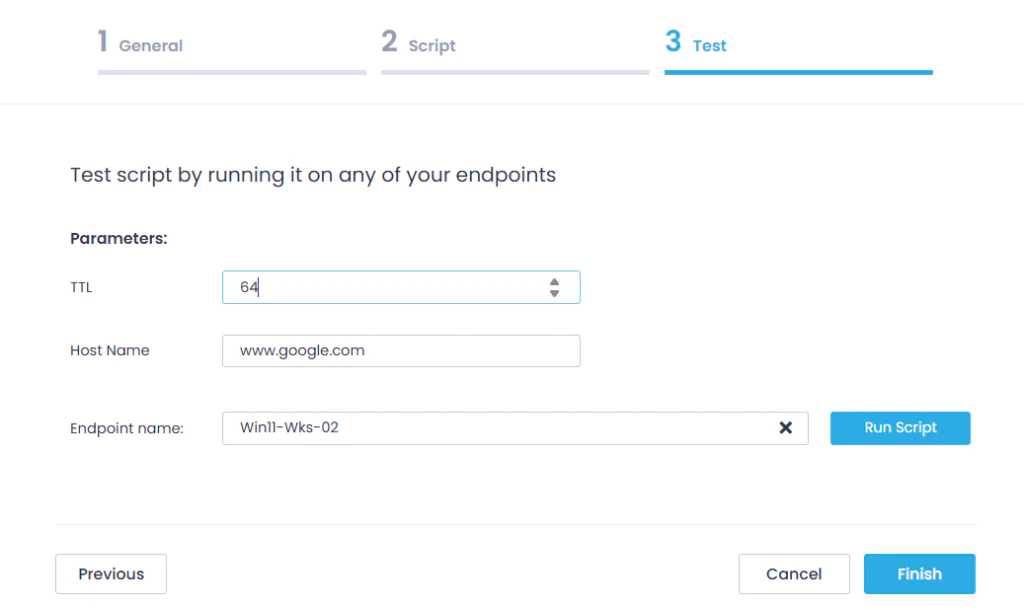
- Finally, on the Test step, select the target endpoint where the script will be executed, and click Run Script.
Tip: For testing purposes, you can enter a nonexistent host name to receive the exit code 245 and see if the reboot is initiated.
After completing the test run, click Finish.
Example 2: CMD
To create a sample CMD script that will send a ping to a certain host with a custom TTL value:
- On the General step of the New Script wizard, enter:
-
- “Ping Host” as Name
- “Send a ping to the specified host.” as Description
- On the Script step, proceed with a sample CMD script:
@echo offping -i %TTL% %Host Name% - In the Parameters section, click +Add parameter and define TTL and Host Name parameters, providing their names, default values, and types:
- Set TTL type to Int and value to 64
- Set Host Name type to String and value to www.google.com
The script will refer to these parameters using %param name% syntax. The parameter values will be passed to the script at run time as environment variables.
- Finally, on the Test step, select the target endpoint where the script will be executed, and click Run Script. After completing the test run, click Finish.
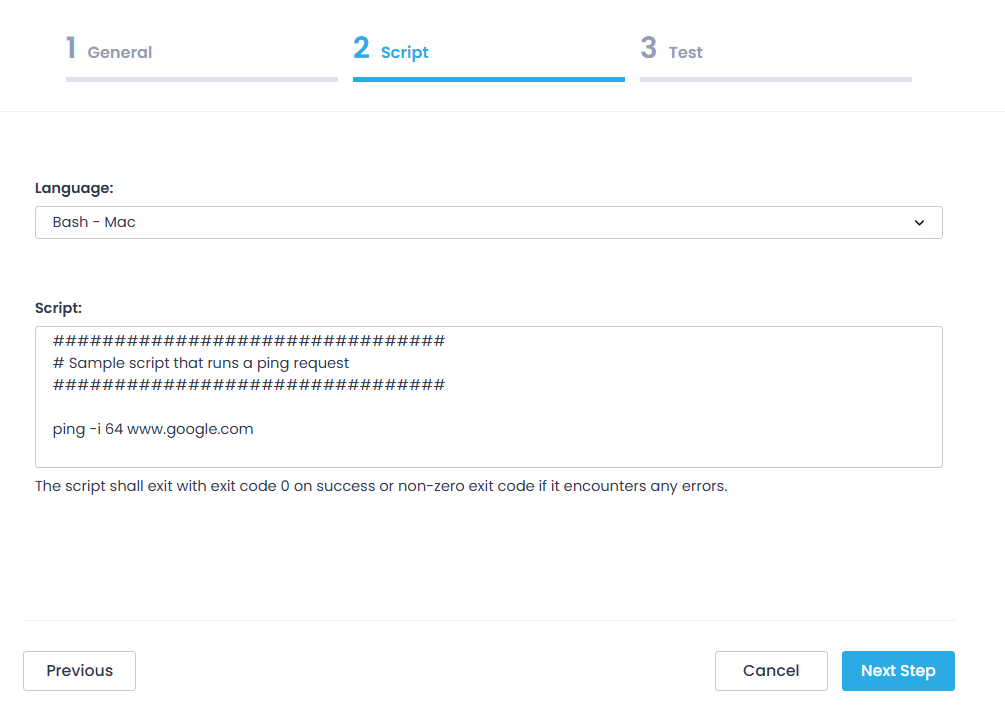
Example 3: Bash
NOTE: Parameter configuration using the wizard is not supported for Bash scripts, so you should provide the required values within the script body.
To add a Bash script that will send a ping to www.google.com with a TTL=64:
- On the General step of the New Script wizard, enter:
- “Ping Host” as Name
- “Send a ping to the specified host.” as Description
- On the Script step, enter:
ping -i 64 www.google.com
NOTE: Reboot option is not supported for Bash scripts.
- Finally, on the Test step, select the target endpoint where the script will be executed, and click Run Script. After completing the test run, click Finish.
Editing or Deleting Scripts
- To modify a built-in script, you should Clone that script using the Actions menu next to it, and then edit the copy.
- To delete your custom script, select it in the Script Library and from the Actions menu, click Delete.
NOTE: Built-in scripts cannot be deleted, as they are maintained by Action1.