Patch Management for Remote Computers
Reasons for Choosing Action1 Patch Management and Remote Control Tools
Many organizations recently switched from in-office to remote work due to the pandemic. Although telecommuting was only meant as a temporary solution to keep businesses running amid the crisis, it’s steadily becoming the new workplace norm. But even now, remote work still causes some unexpected cybersecurity challenges. In a recent survey, 74% of IT decision-makers said remote work makes it harder for employees to follow good security practices.
One of the biggest headaches is ensuring that remote workers use secure software applications on their devices. That’s where remote endpoint management with patches comes in handy. Legacy patching approaches involving manually installing fixes and updates simply don’t cut it in the evolving modern workplace. Since IT teams can’t physically access remote devices and employees can’t fully be trusted to install important security updates, remote patch deployment remains the surefire way to secure distributed endpoints.
1. Reinforce Endpoint Security
Shifting to remote work increases an organization’s attack surface. Sadly, there is very little that businesses can do to avert these risks — besides securing corporate back-end servers and networks. Remote patching helps secure distributed endpoints by ensuring all software applications have the latest security definitions. Remember, endpoint vulnerabilities are easily accessible gateways for cyberattacks.
According to CSO Online, “60 percent of breaches involved vulnerabilities for which a patch was available but not applied”. This is a sobering figure to think that the patch that could have prevented a major data breach was readily available and only needed to be applied. The same report noted, “data breaches cost enterprises an average of $3.92 million.”
As the statistics help to emphasize, even with a remote workforce, patching is not an optional task that organizations can forego, especially during the new normal with no end yet to be seen. The companies must adapt to the new reality quickly. But still, many continue to leverage traditional patch management systems and no longer able to effectively patch remote endpoints.
2. Gain Security Visibility and Control Over Remote Endpoints
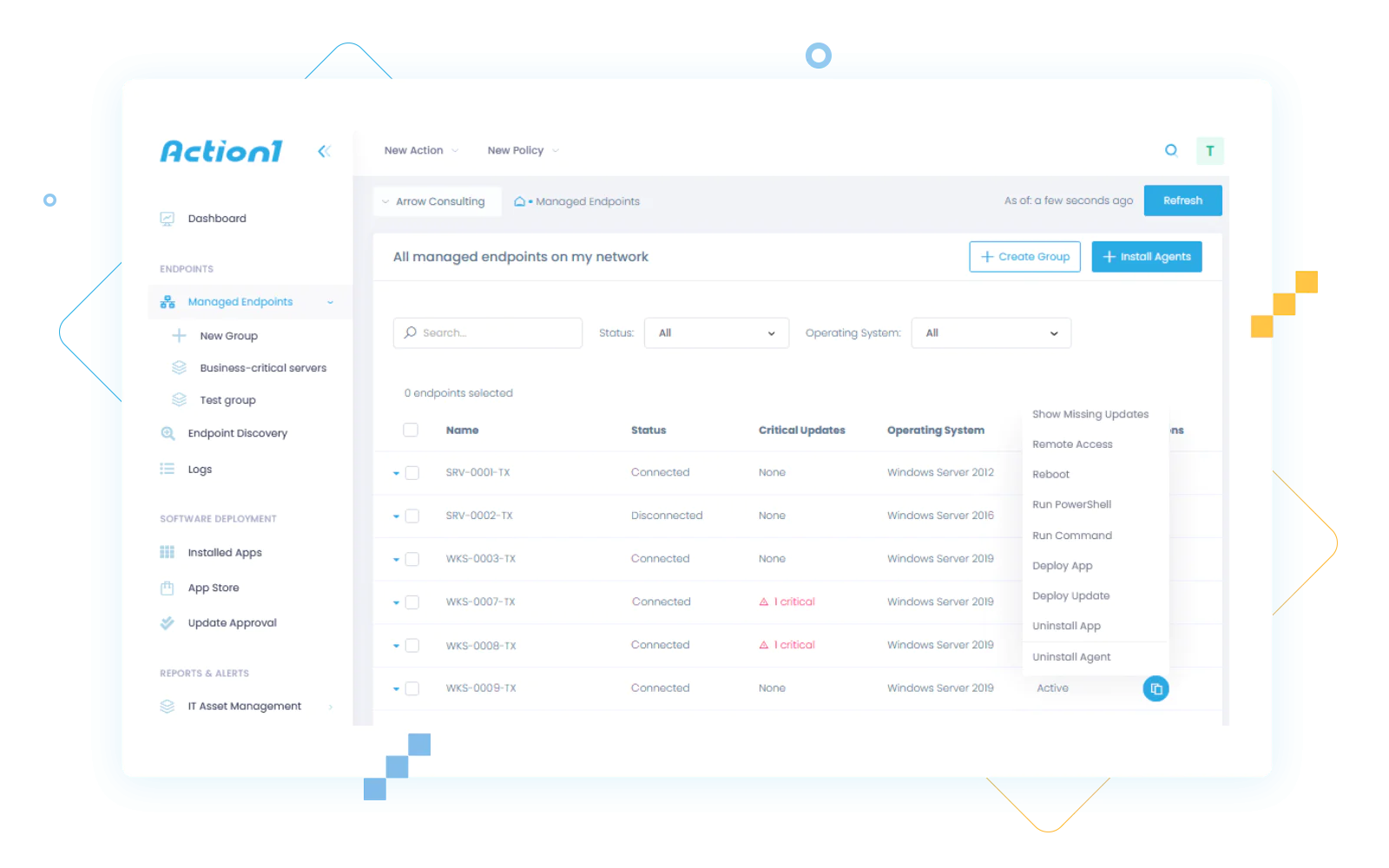
Remote control patch provides basic asset management in a remote and hybrid workforce environment. You can accurately picture the security posture of various endpoints and determine effective solutions for identifiable security gaps. With the right tools, remote patching should give you actionable security insights and a firmer grip on remote end-user devices.
3. Manage The Complete Lifecycles for Multiple Patches
Depending on your staff’s size, you might be looking at dozens to hundreds of unique remote devices. This could mean an overwhelming number of patches to track, source, install and test regularly. And obviously, all this cannot be done manually. Patch management for remote computers simplifies these processes while progressing patches through complete lifecycles.
4. Maintain Remote Work Productivity
Remote patching does not require any technical input from the user. In fact, most of the processes are fully autonomous. So, remote workers don’t have to go out of their way to install software fixes. This saves valuable time and effort. Plus, users and IT teams have more control over when patches can be installed. For instance, IT admins can configure patching policies and schedules based on the most convenient time windows to avoid unnecessary work disruptions.
5. Preserve and Demonstrate Data Security Compliance
A practical patch management plan is a common requirement for various security standards, guidelines, and frameworks, such as NIST 800-171, PCI DSS, and ISO 27001 Annex-A. Software patching is a critical data security responsibility, particularly for those organizations expected to observe strict data protection and privacy rules. For such companies, remote patching not only helps address emerging software vulnerabilities but also maintains and proves security compliance.
Why Legacy Patch Management Tools Are No Longer Effective
When it comes to conventional patch management instruments like Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), these legacy on-premises tools require standard on-premises network connectivity. The corporate network sits behind a perimeter firewall with all the managed resources on the internal network. This type of network connectivity includes traditional layer 2 and layer 3 connectivity via private IP addressing schemes.
In the case of the distributed workforce, remote workers are spread across many external networks. Direct connectivity from WSUS and other conventional on-premises patching software is not possible in the traditional sense. While VPN connections can overcome a few of the hurdles related to external connectivity, it introduces its own issues, including security-related concerns.
Today, remote workers are distributed across discontinuous networks, including personal homes, coworking, and general public spaces. It means there is no direct network connection to their PCs or other devices. From the corporate network perspective, the remote clients appear simply as remote endpoints on the Internet.
With Action1, we are able to support, manage and patch our endpoints no matter where we are, via any device that has a browser. It is a brilliant product that helps us achieve all we wanted in a very cost-effective way.
Patch Management That Just Works
to prevent security breaches and ransomware attacks.




